Caramba
Group 3
For preventative protection against late leaf disease and Fusarium head blight
- Proven protection against Fusarium head blight
- Effective control of later-season foliar diseases
- Reduced deoxynivalenol (DON) contamination to preserve grade quality
Labels & SDS
8 AVAILABLE
Applicable On

Cereals

Corn
Labels & SDS
Benefits of Caramba
- The active ingredient in Caramba is metconazole. Metconazole is part of the triazole (Group 3) family of fungicides which have protective activity on a number of foliar diseases in a range of crops.
- Caramba is a systemic fungicide which means it moves into the plant, as opposed to just staying on the plant surface.
Performance Trials
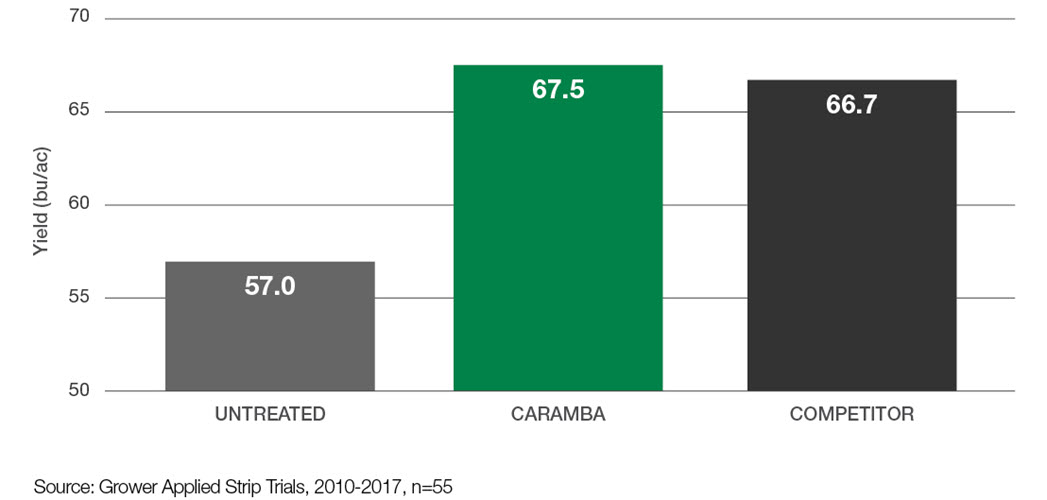
Increased wheat yield with Caramba
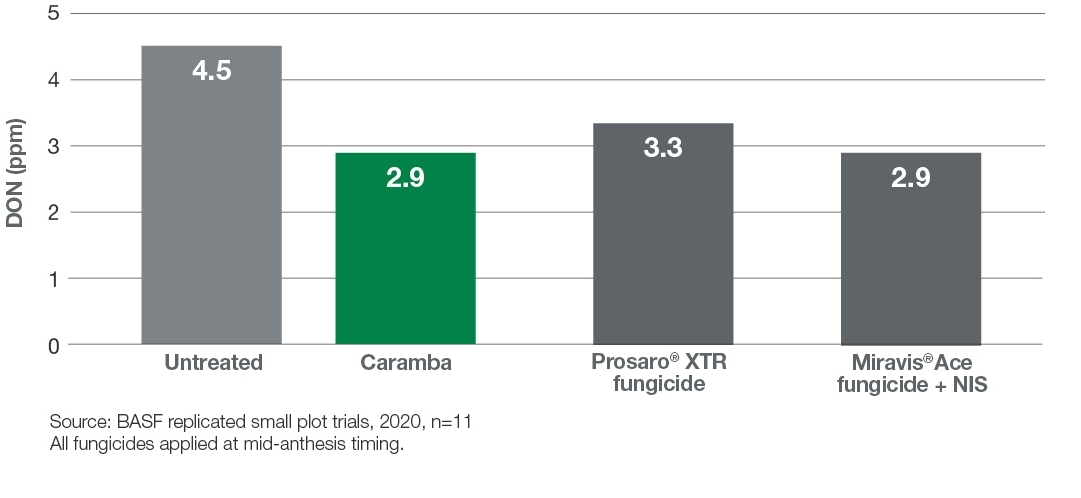
Fusarium head blight management with Caramba
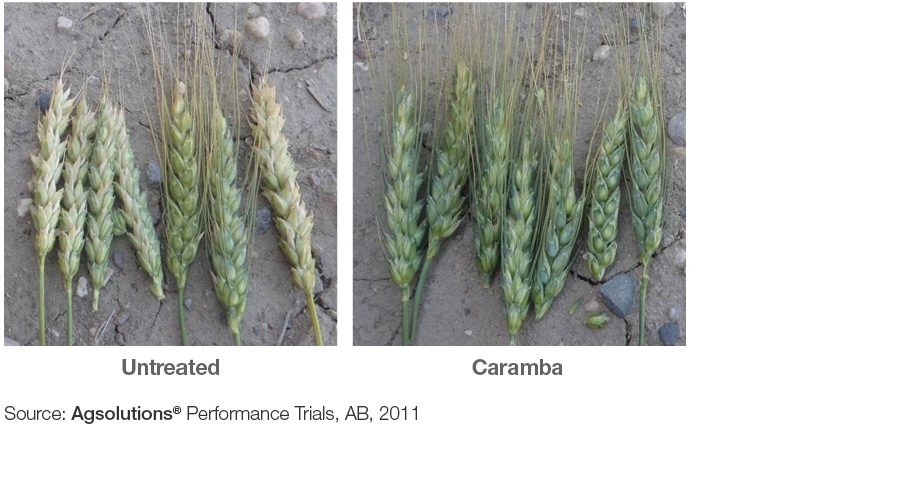

Caramba reduces DON better than the competition
Product Info & Application Guide
Disease Management
Crops |
Diseases |
|---|---|
Barley |
Fusarium head blight (Fusarium graminearum)1 |
Corn (field, sweet, pop, seed types) |
Fusarium ear rot (Fusarium graminearum)1 |
Oats |
Crown rust (Puccinia coronata) |
Rye |
Fusarium head blight (Fusarium graminearum)1 |
Soybeans |
Asian soybean rust (Phakopsora pachyrhizi) |
Sugar beets |
Cercospora leaf spot (Cercospora beticola) |
Wheat (all types incl. durum) and triticale |
Fusarium head blight (Fusarium graminearum)1,2 |
1 Suppression only.
2 Not suppressed or controlled in triticale. Wheat only.
Application Tips
Rainfastness – 1 hour.
- Caramba should be applied preventatively, prior to the onset of disease.
- Avoid application when heavy rain is forecast.
- Apply when conditions are favourable for disease development.
Pre-harvest interval
- 7 days after application for sweet corn (mechanical harvesting only).
- 18 days after application for sweet corn (hand harvesting only).
- 20 days after application for pop and field corn.
- 30 days after application for barley, oats, rye and wheat.
When to Apply
| Crops |
Staging |
|---|---|
Barley |
full head emergence to 3 days after full emergence3 |
Corn (field, sweet, pop, seed types) |
full silking to silk browning4 |
Oats, rye, triticale, wheat (all types incl. durum) |
20% flower3,5 |
3 For suppression of fusarium head blight and leaf disease control at heading. For leaf disease control prior to heading, apply before the appearance of symptoms.
4 This is BBCH stage GS 63-67.
5 This is BBCH stage GS 61-63.
How Much to Apply
One case of Caramba fungicide will treat 40 acres at the fusarium rate and 60 to 80 acres6 at the cereal leaf disease rate.
One shuttle treats 320 acres at the fusarium rate.
One tote treats 1,000 acres at the fusarium rate.
For fusarium head blight, fusarium ear rot, gibberella ear rot |
405 ml/ac (1 L/ha) |
For cereal leaf diseases |
202 to 283 ml/ac (500 to 700 ml/ha)6 |
6 These rates should be used only for leaf disease control prior to heading. They are not recommended for applications targeting fusarium head blight, fusarium ear rot or gibberella ear rot.
Water Volume
Ground application |
40 L/ac (10 gal/ac) |
Aerial application |
20 L/ac (5 gal/ac) |
Mixing order
- Ensure the spray tank is clean before use.
- Fill the spray tank 1/2 full of water and start agitation.
- Add the required amount of Caramba fungicide to the tank.
- Continue agitation while filling the remainder of the spray tank.
- After use, clean the spray tank according to label precautions.
FAQ
What diseases are controlled by Caramba?
The diseases controlled by Caramba are as follows:
- In barley - Fusarium head blight (Fusarium graminearum)1, leaf rust (Puccinia hordei ), net blotch (Pyrenophora teres), powdery mlidew (Erysiphe graminis), scald (Rhynchosporium secalis), spot blotch (Cochliobolus sativus)1, and stripe rust (Puccinia striiformis)
- In corn (field, sweet, pop, seed types) - Fusarium ear rot (Fusarium graminearum)1, and gibberella ear rot (Gibberella zeae)1
- In oats - Crown rust (Puccinia coronata), fusarium head blight (Fusarium graminearum)1, and septoria leaf blotch (Septoria avenae)
- In rye - Fusarium head blight (Fusarium graminearum)1, leaf rust (Puccinia recondita), powdery mildew (Erysiphe graminis), and stripe rust (Puccinia striiformis)
- In wheat (all types incl. durum wheat) and triticale - Fusarium head blight (Fusarium graminearum)1,2, leaf rust (Puccinia recondita), powdery mlidew (Erysiphe graminis f. sp. tritici), septoria glume blotch (Stagonospora nodorum), septoria leaf spot (Septoria tritici or Stagonospora nodorum), spot blotch (Cochliobolus sativus)1, stem rust (Puccinia graminis), stripe rust (Puccinia striiformis), and tan spot (Pyrenophora tritici-repentis )
1. Suppression only. 2. Not suppressed or controlled in triticale. Wheat only.
How do I determine the best timing for a fungicide application on my cereals (i.e. flag-leaf timing vs. heading)?
To determine the best time to apply a fungicide, you must determine your risk levels and production goals.
In wheat, 65% of yield potential is built by the last two leaves. That's why growers see the most consistent return by planning a preventative fungicide application on their cereals at flag-leaf.1 A planned application of Nexicor® consistently provides industry-leading performance and a positive return under high and low foliar disease pressure.2
If you are at risk of fusarium head blight (FHB), BASF recommends an application of Caramba® fungicide at 20% flowering (GS 61-63). Caramba can help reduce deoxynivalenol (DON) contamination and preserve grade quality. Caramba also provides an extended window for effective control of later-season foliar diseases.
1. While Nexicor fungicide can be applied between stem elongation and early head emergence (GS 31-55), research suggests that applying at flag-leaf (GS 37-39) helps maximize yield potential in cereals.
2. AgSolutions® Performance Trials, Western Canada 2016-2017
What is the optimal timing for fusarium head blight (FHB) control in cereals?
To maximize yield and suppress FHB, apply Caramba® fungicide to wheat, oats and rye when crops are at 20% flowering (GS 61-63). For barley, apply Caramba between full head emergence to up to three days after full emergence of main stem heads.


