Cotegra
Group 7 & 3
The standard for sclerotinia management.
- Combines two leading active ingredients that target sclerotinia in a convenient liquid premix
- Outperforms competitors, preserving yield
- Outperforms competitors under the toughest conditions
Labels & SDS
6 AVAILABLE
Applicable On

Canola

Field Peas

Lentils

Soybeans
Labels & SDS

Target yield – Understanding yield targets will help determine the potential impact of sclerotinia and help quantify the value of a sclerotinia fungicide application

Crop rotation – Seeding canola more frequently than every 1 in 3 years of a rotation or having a tight rotation with other host crops for sclerotinia (pulses) can increase risk

Commodity price – High commodity prices further benefit the return on investment (ROI) when applying fungicides
Weather – Wet conditions create the ideal environment for sclerotinia development, but morning dew and the transition from hot days to cool nights can also create high humidity in the crop canopy
Benefits of Cotegra
Cotegra fungicide inhibits spore germination and also inhibits mycelial growth and sporulation of the fungus on the leaf surface. It can be applied in either pre- or post-infection, however, optimum disease management is achieved when it is applied preventatively in a scheduled protective spray program.
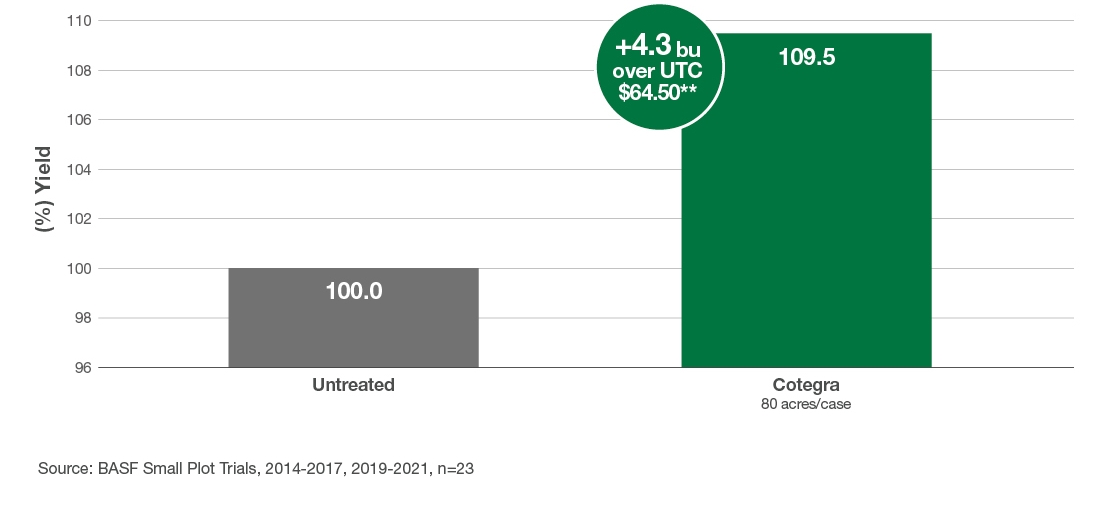
Performance Trials
Cotegra premium performance
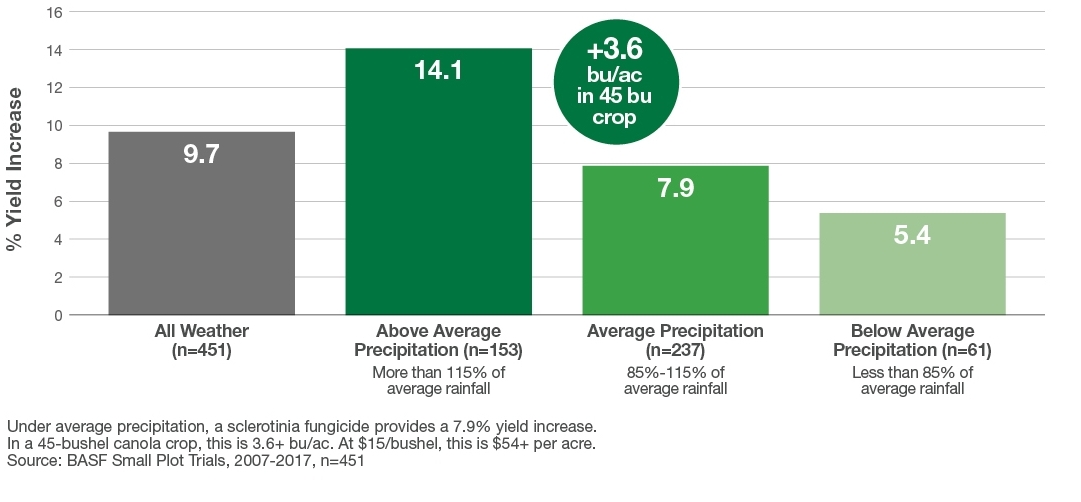
Sclerotinia fungicide return in canola across varying weather conditions
Product Info & Application Guide
Disease Management
| Crops |
Diseases managed |
|---|---|
| In canola, oriental mustard, rapeseed. | Sclerotinia stem rot (Sclerotinia sclerotiorum)2 |
| In chickpeas. | Ascochyta blight (Ascochyta rabiei)2 White mold (Sclerotinia sclerotiorum)3 Grey mold (Botrytis cinerea)3 |
| In dry beans. | White mold (Sclerotinia sclerotiorum)3 |
| In field peas. | Mycosphaerella blight (Mycosphaerella pinodes)4 Ascochyta blight (Ascochyta pinodes)4 White mold (Sclerotinia sclerotiorum)5 |
| In lentils. | Anthracnose (Colletrotrichum lentis)4 Grey mold (Botrytis cinerea)5 White mold (Sclerotinia sclerotiorum)6 |
| In soybeans. | Asian soybean rust (Phakopsora pachyrhizi)2 Frog eye leaf spot (Cercospora sojina)2 Septoria brown spot (Septoria glycines)3 White mold (Sclerotinia sclerotiorum)3 |
1 Dry beans include Lupinus spp. (grain lupin, sweet lupin, white lupin, white sweet lupin), Phaseolus spp. (field beans (dry common and coloured beans) such as kidney, black, cranberry, pink, navy bean, pinto bean, tepary bean, lima bean (dry)), Vigna spp. (adzuki bean, blackeyed pea, catjang, cowpea, crowder pea, moth bean, mung bean, rice bean, southern pea, urd bean, broad or faba bean (dry)).
2 Control.
3 Suppression.
4 Suppression at the low rate of 80 ac/case (0.6 L/ha) and control at the high rate of 70 ac/case (0.7 L/ha).
5 Suppression at the high rate of 70 ac/case (0.7 L/ha).
6 Control at the high rate of 70 ac/case (0.7 L/ha).
Application Tips
Rainfastness
- Avoid applying when rain is forecasted within 3 hours of application.
Pre-harvest interval
- 36 days after application for canola, oriental mustard and rapeseed.
- 21 days after application for lentils, field peas, chickpeas, dry beans, and soybeans.
When to Apply
Crop |
Staging |
|---|---|
Canola, Oriental mustard, rapeseed |
20 - 50% flowering |
Chickpeas, field peas, lentils |
Beginning of flowering or at first sign of disease* |
Dry beans |
20 - 50% flowering |
Soybeans |
Prior to disease development (late R1/R2 to R3) |
*If planned as a second application, apply 7-14 days after the first application, depending on weather conditions and disease severity.
How Much to Apply
One case of Cotegra fungicide will treat 50 to 80 acres, depending on crop.
| Crop | Rate |
|---|---|
Canola, field peas, lentils, oriental mustard, rapeseed7 |
240 - 280 ml/ac (0.6 - 0.7 L/ha) |
Chickpeas, soybeans |
280 ml/ac (0.7 L/ha) |
Dry beans |
400 ml/ac (1 L/ha) |
Water Volume
Ground application8 |
40 L/ac (10 gal/ac) minimum |
Aerial application |
20 L/ac (5 gal/ac) minimum |
7 Use the high rate for canola, oriental mustard and rapeseed and the control of anthracnose on lentils if weather conditions are favourable for disease development (i.e. high humidity/moisture) and/or when risk for disease development is high (i.e. narrow host rotation with disease history and high potential for inoculum).
8 Higher water volumes recommended for optimal coverage.
Mixing Order
- Fill the cleaned spray tank 1/2 full of water and start agitation.
- Add the required amount of Cotegra fungicide to the tank.
- Continue agitation while filling the remainder of the spray tank.
- After use, clean the spray tank according to label precautions.
FAQ
What are the scouting tips to assess sclerotinia risk?
- Around mid-June through flowering, look for apothecia (golf-tee shaped mushroom structures) under the canopy. Ascospores are shot in the air from apothecia, and once in the air they move on wind currents locally and to adjacent fields. Ascospores are what infect canola plants to cause sclerotinia infections.
- Weather: cool, moist, humid periods increase risk. If when walking through your canola field late-morning or early-afternoon and the plants are still wet, risk is elevated.
- Risk also increases with these factors:
- Number of sclerotinia susceptible crops planted in past 3-4 years of rotation
- Density of canopy; healthy vigorous crops have higher risk
- Previous sclerotinia disease incidence, either in canola or other host crops
What are the symptoms to scout for when identifying sclerotinia?
Scouting for sclerotinia symptoms on plants begins at the end of flowering and continues through harvest timing. A couple of weeks after initial sclerotinia infection, watery lesions or light brown discoloration can be seen on leaves, stems and branches. These lesions expand and cause canola stems to ‘bleach’, taking on a whitish appearance, a major characteristic of sclerotinia infections in canola.
When the bleached stems are split open later in the season, sclerotia can often be found. Sclerotia are the hard, dark resting bodies of sclerotinia that overwinter in the soil.
When is the best time to apply a fungicide on my canola crop?
Nexicor® fungicide should be applied at the 2 to 6 leaf stage to protect the plant from blackleg infection and provide Plant Health Benefits1.
Lance® and Cotegra® fungicides should be applied at the 20-50% flowering stage to protect the plant from sclerotinia infection.
1Plant Health Benefits refer to products that contain the active ingredient pyraclostrobin.
Where can I find the tank cleaning recommendations?
Tank clean-out recommendations can be found on product labels.
What are the differences between Cotegra®, Lance® and Nexicor® fungicides?
Nexicor fungicide provides high-level control of blackleg in canola and contains three active ingredients, including Groups 3, 7 and 11. Nexicor builds on proven Plant Health Benefits1 to increase growth efficiency and help better manage minor stress, leading to greater yield potential2. It should be applied at the 2 to 6 leaf stage of canola.
Cotegra fungicide contains prothioconazole and boscalid, two leading active ingredients, and is the standard for sclerotinia management.
Lance fungicide contains boscalid, a Group 7 active ingredient and provides proven and consistent yield protection from sclerotinia and alternaria black spot. Both Lance and Cotegra can be applied at the 20-50% flowering stage.
1 Plant Health Benefits refer to products that contain the active ingredient pyraclostrobin.
2 All comparisons are to untreated, unless otherwise stated.
What are the recommended water volumes and application rates for canola fungicides?
- For ground applications with Cotegra, Lance or Nexicor fungicides, the minimum water volume is 10 gal/ac (100 L/ha). Higher water volumes are recommended for optimal coverage.
- For aerial applications, the recommended water volume for all BASF canola fungicides is 50 L/ha (5 gal/ac).
What are the best conditions to look for when applying Cotegra® fungicide on canola?
Ideal applications are moderate temperatures (lower than 28oC) and low wind. Avoid application when rain is forecasted within 3 hours of application.
Restrictions/conditions for Cotegra fungicide application in canola:
- DO NOT apply during periods of dead calm.
- Avoid application of this product when winds are gusty.
- For aerial application, DO NOT apply when wind speed is greater than 16 km/hour at flying height at the site of application.
- DO NOT apply with spray droplets smaller than the American Society of Agricultural Engineers (ASAE) medium classification. For ground application, boom height must be 60 cm or less above the crop or ground.
- For aerial application, to reduce drift caused by turbulent wingtip vortices, the nozzle distribution along the spray boom length MUST NOT exceed 65% of the wing- or rotor-span.
Can I still apply Cotegra fungicide on canola that is at the late flowering stage?
Cotegra fungicide is most effective when applied at the recommended 20-30% flowering stage. That said, late flowering applications can still provide value. Per label guidelines, Cotegra applications are allowed on canola from 20% flowering up until full bloom.
At which crop stage should I be spraying a fungicide on canola?
- If you're using Nexicor fungicide, you should spray between the 2-leaf and 6-leaf stage.
- For Cotegra and Lance fungicides, you should spray between 20-50% flowering.




